
- #Adaptive immune repertoire sequencing data repositiry full
- #Adaptive immune repertoire sequencing data repositiry software
#Adaptive immune repertoire sequencing data repositiry full
It is also important to think about how molecules from the full repertoire get included into the pool to be amplified for sequencing. Sequences, where errors and somatic hypermutation (SHM) are often indistinguishable. Without UMIs, it is advisable to cluster highly similar reads to avoid overcounting, particularly for IG
#Adaptive immune repertoire sequencing data repositiry software
Protocols may also require particular matched software tools to fully utilize the advantages of those schemes.
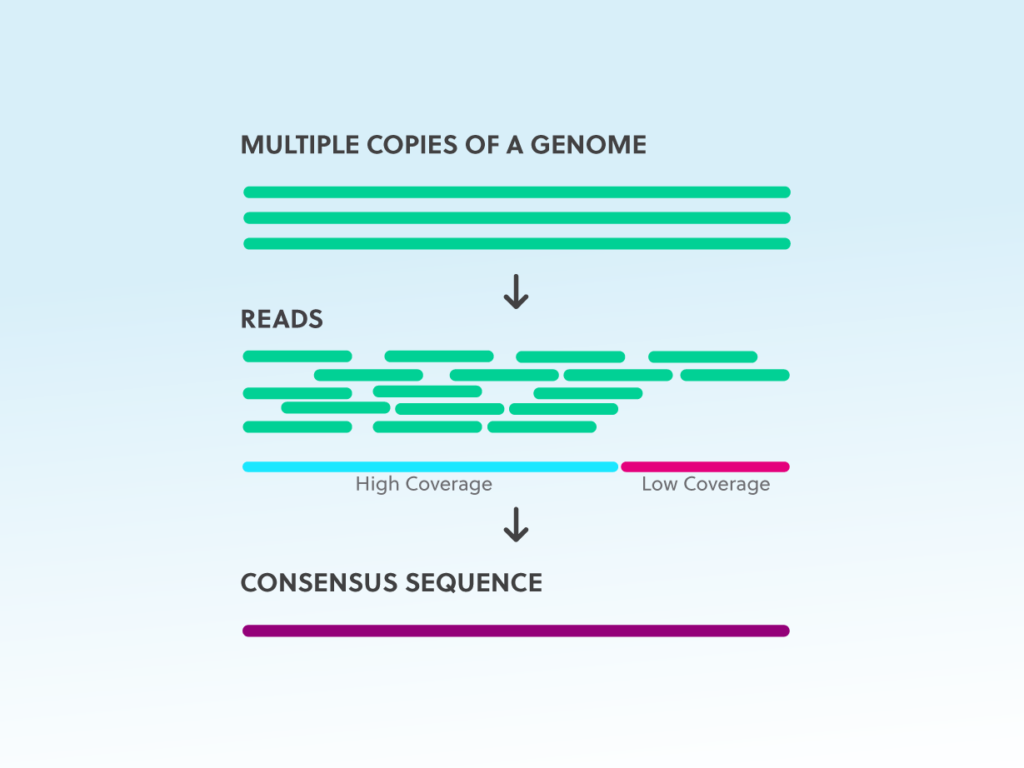
UMIs can also be used to improve quantification, by collapsing apparent expansions due to differential amplification. UMIs may also be used when sequencing DNA, but that is currently less common in practice. Of note, while the usage of UMIs enables experimental error correction, their usage necessitates a considerably larger sequencing depth due to consensus read building (for a more nuanced discussion, see, e.g., ).
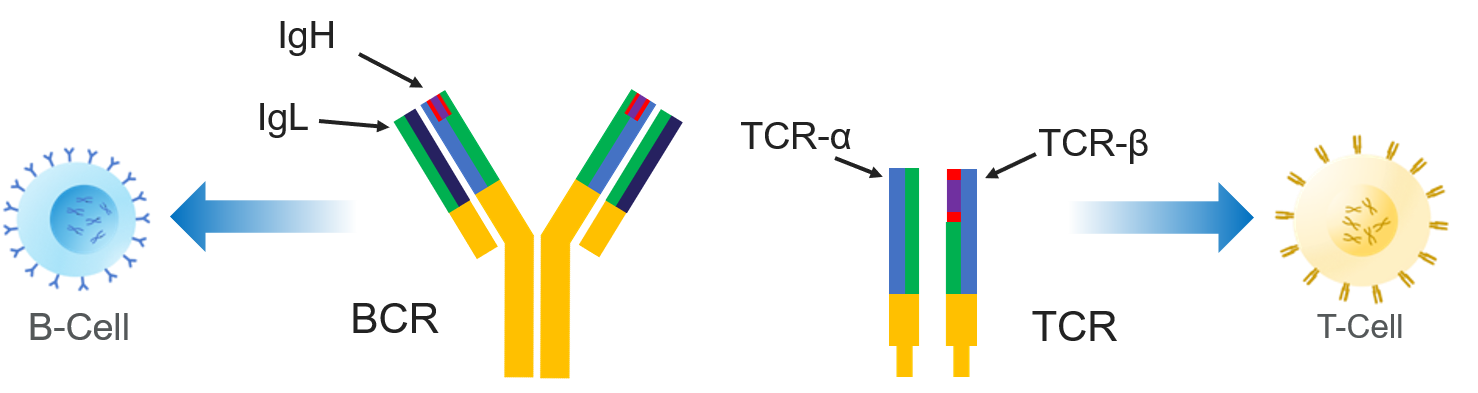
When amplifying mRNA, the initial molecules may also be labeled with UMIs, which enable the correction of errors introduced by PCR and/or sequencing by identifying reads that are derived from the same original molecule. They may have been initially amplified from genomic DNA or from mRNA the former results in exactly one initial copy of each productive V(D)J rearrangement in a cell, while the latter starts with several or many copies and may vary with cell type and activation state. The most critical set of considerations revolve around the origins of the molecules that were actually loaded into the sequencer ( see Chap. In such a case, it may be useful to work within a particular ecosystem like Immcantation ( ), VDJServer, or SONAR, which provide several tools for a thorough analysis from quality control to clonal analysis, to facilitate smooth workflows. In addition, interest in specialized inquiries like phylogenetic analysis of IGs or calculation of clonal dynamics may require additional specific tools.
While many tools such as MiXCR, IMGT, and others (Table 1) can handle both types of data, some are specific to one or the other. In addition, thought must be given to what computational and storage resources will be necessary given the size of the dataset and the intended analysis.Ī clear first decision point in AIRR-seq data analysis is whether IG Each of these alternatives may require (or preclude) the use of certain software tools and influence the interpretation of the analysis. AIRR-seq data to be analyzed may have been generated from genomic DNA or mRNA, with or without unique molecular identifiers (UMIs), and in bulk or single-cell context, as described in the Chap. Many of the same factors that influenced choices in experimental design will be important in planning the computational approach as well. 15, attention turns to analyzing the data collected to produce biological insights. Of key terms) experiment has been successfully designed and carried out (see discussion in the Chap. Once an Adaptive Immune Receptor Repertoire sequencing (AIRR-seq, please see the AIRR Community glossary at doi: for definitions We also highlight a number of common difficulties with common AIRR-seq data processing and provide strategies to address them. In this chapter, we outline key factors to consider when preprocessing raw AIRR-Seq data and annotating the genetic origins of the rearranged receptors.
Analyzing AIRR-seq data can prove challenging even with high-quality sequencing, in part due to the many steps involved and the need to parameterize each step. Recent advancements in the technology include sequencing at the single-cell level and in parallel with gene expression, which allows the introduction of multi-omics approaches to understand in detail the adaptive immune response. Since the method was first introduced in 2009, AIRR sequencing (AIRR-Seq) has been applied to survey the immune state of individuals, identify antigen-specific or immune-state-associated signatures of immune responses, study the development of the antibody immune response, and guide the development of vaccines and antibody therapies. High-throughput sequencing of adaptive immune receptor repertoires (AIRR, i.e., IG and TR) has revolutionized the ability to carry out large-scale experiments to study the adaptive immune response.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
